A secured loan is one in which the borrower must provide collateral as an asset to receive the loan. A high-value item, such as a home, automobile, or jewelry collection, is often used as collateral to get a loan. Lenders seize assets to recoup losses incurred if a borrower defaults on a loan.
One of the key reasons for the relevance of secured loans is making it possible for borrowers who otherwise need access to credit to meet the requirements for an unsecured loan to have access to credit. The interest rates on secured loans are often lower than those on unsecured loans. It is because the lender takes the collateral if the borrower fails.
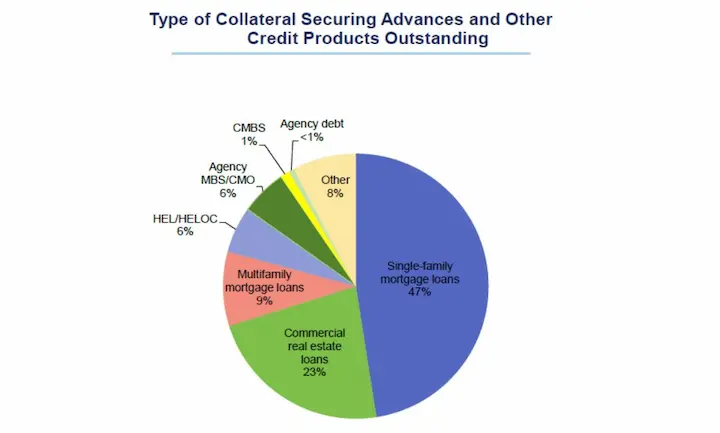
Many types of loans fall under the secured loans category, including Mortgages, Auto loans, Loans from Pawn shops, Home Equity Loans, and Personal loans.
What is a Secured Loan?
Secured loans are those that need collateral to be disbursed. The borrower pledges an asset to the lender as collateral for the loan. Collateral is often anything of high monetary value, such as a vehicle or jewelry. The interest rate for Secured loans is lower than for unsecured loans. Home mortgages, auto financing, and pawnshop loans are all secured loans. Credit reports are crucial in determining loan eligibility and interest rates.
How Does Secured Loan Work?
To acquire a secured loan, the borrower must offer collateral like a vehicle, home, or other valuable property. The lender evaluates the borrower’s collateral to decide how much to lend. The interest rate and repayment schedule depend on the borrower’s creditworthiness and the collateral’s value. Lenders typically review credit reports to assess creditworthiness. Examine the capacity to make payments and research the loan conditions before accepting a secured loan.
What Is the Purpose of Secured Loans?
Borrowers prefer secured versus unsecured loans since the former usually offers more reasonable interest rates. Secured loans help minimize the lender’s risk since the lender takes the collateral if the borrower defaults. Useful for significant purchases like houses or cars, the collateral’s value must be at least as high as the loan’s total cost to the borrower for this sort of loan to be considered a good investment. Additionally, business loans can be taken out as secured loans to help grow a company.
What Are the Different Types of Secured Loans?
Below are some typical types of secured loans for one’s consideration, including business loans.
1. Bad Credit Loans
Bad credit loans are for borrowers with low credit ratings or limited credit history. These loans are challenging to acquire and have higher interest rates and fees than others. Comparing poor credit loans to discover the best terms and prices is crucial.
2. Business Loans
Business loans are a type of secured loan that can help finance operations, growth, and other essential aspects of a company. Both startups and established businesses can benefit from these loans, which usually require collateral like equipment, inventory, or real estate. Business owners should shop for the best rates and terms for their needs.
Consider the financial situation. A car title loan is a good idea since it’s a fast and easy method to borrow cash but risky. The total cost of a vehicle title loan is greater than any other loan in terms of interest and fees. The requirement for a dependable form of mobility becomes apparent in the event of a loan default and subsequent repossession of the borrower’s vehicle.
3. Secured Credit Cards
Secured credit cards are for persons with poor credit or no credit history who can’t get a standard card. It helps one develop credit if used carefully. Pay the payments on time and maintain the balance below the limit to achieve this.
4. Mortgage Loans
A mortgage is a loan to acquire real estate. Collateral backs it. The borrower and lender agree that the residence is the collateral for the loan. The lender has the legal right to seize the collateral if borrowers cannot repay the loan.
Mortgages are often understood as loans taken out to purchase a house; however, mortgages are obtained to finance the acquisition of other kinds of land or property. Borrowing money against the current house’s value is called “refinancing” the mortgage.
5. Vehicle Loans
A Vehicle loan is used to buy cars. Banks, credit unions, and other entities provide secured and unsecured vehicle loans.
6. Life Insurance Loans
A policy backs life insurance loans. Permanent life insurance with cash value is borrowed against. The lender retains the policy as security until the debt is paid off.
Life insurance loans are a dangerous method to get cash quickly. The lender seizes the life insurance policy if one defaults on the debt and the beneficiaries do not obtain the full death benefit. A life insurance policy’s cash value and death benefit are reduced to account for any loans and interest taken out against the policy.
7. Pawnshop Loans
Pawn shop loans are a good option for borrowers who need a quick and easy way to borrow money and have valuable items used as collateral. Pawn shop loans are a fantastic alternative for borrowers with less-than-ideal credit since they are simpler to qualify for than other loans. Pawn shops lend money against collateral, such as jewelry or other valuables.
8. Secured Lines of Credit
A line of credit is a flexible loan from a financial institution that consists of a predetermined amount of money borrowed as required and return immediately or over time. Line of Credit is a lower-risk revenue stream than credit card loans. Unregulated outstanding sums affect a bank’s earning asset management.
9. Share-secured or Savings-secured Loans
Share-secured loans use stock or other assets as collateral. Lenders hold the borrower’s shares or securities as loan collateral. Both share- and savings-secured loans help borrowers develop or repair credit. The collateral reduces the lender’s risk, increasing the borrower’s approval chances. Lenders forfeit the loan’s collateral if the borrower fails.
What Can Be Used as Collateral for a Secured Loan?
The borrower agrees with the lender to pledge an asset, known as collateral, as security if the borrower cannot repay the loan. Here are examples of popular forms of collateral used to secure a loan.
- Real Estate. Real estate examples are A house, a business building, or even land.
- Personal Property. Personal property includes automobiles, jewels, artwork, or other expensive objects that are readily marketable if required.
- Bank Accounts. The borrower utilizes the checking or savings account as collateral.
- Bonds or Stock. Bonds and stocks are financial market securities. Both bonds and stocks are used to raise funds for companies and governments.
- Business Assets. Equipment, inventory, or accounts receivable are used as collateral for a loan by a business.
Remembering that the collateral’s value must be equivalent to the amount borrowed for the loan to be approved is essential. The lender must be able to recoup the loan amount from the sale of the collateral if the borrower fails to repay the loan and the lender is forced to sell the collateral.
What Will Happen to the Collateral if the Lender Is Not Paid in a Secured Loan?
Secured lenders have the legal power to repossess the collateral to guarantee the loan if the borrower fails to repay the debt in full. It allows the lender to liquidate the collateral and recoup any remaining loan balance. The lender must foreclose to sell the property and recoup the unpaid principal if the loan was secured by real estate. The borrower has the right to pay off any remaining balance on the loan even after the lender has repossessed the collateral. The collateral is returned to the borrower if the loan is repaid.
What to Do if the Borrower Fails to Pay the Secured Loan?
Borrowers in financial trouble contact lenders to negotiate repayment. Consider arranging a new payment plan or a temporary discount. Visit a financial advisor or credit counseling agency if the borrower and lender can’t agree.
1. Contact the Lender for a Secured Loan
Borrowers experiencing trouble making payments on a secured loan must contact the lender as soon as feasible. Lenders usually are reached through phone, email, or a dedicated website. The loan status is verified over the phone by asking for identification and bank details.
2. Set Priorities for Your Payments
Prioritize loan payments if one needs to help pay all to guarantee the most crucial bills are paid first. High-interest debts, like student loans, are paid off first since one costs more overall. Late fines are paid in full before any further payments are made. Late payments affect credit scores, so pay off debts to protect them. Consider personal and financial goals while prioritizing payments, especially when dealing with student loans.
3. Obtain Financial Assistance
Credit counseling services guide and support clients in debt management and developing spending plans. It negotiates with creditors to lower interest rates or monthly payments, including those for student loans.
What are the Pros and Cons of a Secured Loan?
Lenders feel more comfortable extending credit when having something of value to put up as collateral.
Pros
- A secured loan’s interest rate is lower than an unsecured loan since the lender takes less risk. The borrower finds the debt more manageable as a result of this.
- Secured loans provide more flexible repayment terms than unsecured loans, giving borrowers greater leeway to create a repayment plan that best suits one’s budgetary needs.
- Loan amounts are higher with secured loans than the unsecured counterparts. The lender has something to utilize as compensation if the borrower cannot repay the loan.
Cons
- Collateral is at risk if the borrower fails on the loan and the lender exercises the right to repossess the collateral. It implies that if the borrower defaults on the loan, he risks losing the home, vehicle, or other valuables to the lender.
- Borrowers are limited in choosing a lender since not all lenders provide secured loans.
- The procedure is more complicated as the borrower transfers collateral to the lender in a secured loan: the time it takes and the paperwork it necessitates to get a loan increase.
Below are some statistics on collateral for secured loans:
| Statistic | Value |
|---|---|
| The second most common type of collateral | Real estate (60%) |
| It must be greater than the amount of the loan | Vehicles (25%) |
| Average interest rate | Secured loan (8%), Unsecured loan (12%) |
| Approval rate | Secured loan (60%), Unsecured loan (40%) |
| The second most common type of collateral | It must be easy to sell |
| Collateral must be liquid | Must be easy to sell |
| Collateral must be insured | To protect the lender |
What are the Best Secured Loan Lenders?
Many lenders offer secured loans, including banks, credit unions, and online lenders. Some of the best lenders for collateral loans offer competitive interest rates, flexible repayment terms, and good customer service.
Quick Access to Cash
Payday loans and online loan applications provide borrowers with fast access to much-needed cash, which is crucial in times of financial emergencies or unexpected expenses.
Convenience
For individuals who require a small loan for a short period, or those who prefer the convenience of online applications and lack access to other credit forms, payday loans can be a useful option.
Fewer Requirements
Payday advances and online loan applications usually have less stringent eligibility criteria compared to conventional loans, making them accessible to a broader range of individuals.
What is the Average Interest Rate for a Secured Loan?
The average interest rate on a secured loan differs from one borrower to the next and from one lender to the next based on the value of the Collateral, the lender’s risk, the borrower’s credit history, and the loan length.
Secured loans offer lower interest rates than unsecured loans since the lender has less risk. Federal Reserve statistics show that the average secured loan interest rate in 2022 was 4%. Borrowers’ interest rates are greater or lower, depending on the circumstances.
How to Get a Secured Loan?
Getting a secured loan normally requires proof of income and passing a credit check. Furthermore, borrowers must put up some Collateral, a property, a car, or other valuable items. The amount to borrow depends on the collateral’s value, which the lender determines.
- Pick out the loan needed and the asset used as collateral.
- Find loan providers who provide the necessary amount and compare the rates and conditions.
- Gather supporting documentation, including identity, income, and collateral ownership evidence.
- Fill up a loan application and deliver it to the lender with the necessary paperwork and security.
- The lender is currently reviewing the application.
- Check the loan terms before applying.
- Deliver the promised collateral to the lender in exchange for the loan money.
- Start paying payments as agreed upon in the loan arrangement.
What Are the Requirements to Get a Secured Loan?
Lenders use several criteria to decide whether or not to provide a secured loan. Some examples are:
- Collateral: Most secured loans need the borrower to put up some security, such as a home or vehicle, as collateral. As such, the collateral’s value is included in the loan’s total amount and conditions.
- Credit history: Lenders often check a borrower’s credit history to see whether one’s are a good risk and whether or not the borrower must repay the loan. The lender is more likely to provide the loan if the borrower has good credit.
- Income: The ability to repay the loan is one factor that lenders consider, along with the borrower’s job history and income. The likelihood of getting a loan rises if one has a regular source of income.
- The debt-to-income ratio measures monthly debt payments as a proportion of monthly income. Lenders use this percentage to determine a borrower’s repayment probability.
- Loan Uses: The lender considers the loan’s intended use while deciding. Some secured loans, including those for home improvements and automobiles, have strict eligibility requirements.
- Loan term: A loan’s duration impacts the interest rate and other associated fees. The monthly payments on a longer-term loan are cheaper, but the interest rate is greater than on a shorter-term loan.
- Fees: Lenders charge fees for services in arranging the loan’s origination, closure, and other areas. The borrower has to know all the fees included with the loan before agreeing to the conditions.
How Long Does It Take to Process a Secured Loan?
The time it takes to complete a secured loan varies based on several circumstances, such as the lender, the kind of loan, and the borrower’s financial status. The loan process takes as little as a few days or as much as a few weeks, depending on the circumstances.
The processing time for a secured loan varies, but generally, the procedure is a lot more practical when compared to the processing time for other kinds of loans, such as a mortgage.
Is It Hard to Qualify for a Secured Loan?
No, secured loan requirements differ from one lender or product to the next. However, because the borrower is providing collateral to secure the loan, being approved for a secured loan is simpler than getting approved for an unsecured loan. Lenders still look at factors before deciding to provide a secured loan. The borrower’s credit, income, debt-to-income ratio, and collateral worth play a role.
A secured loan is accepted if the applicant has a solid credit history, consistent income, and enough collateral. A secured loan is more challenging to get, however, if the applicant needs a higher credit score or adequate collateral.
Does Credit Score Affect Your Secured Loan Application?
Yes, credit affects secured loan applications. Collateral backs secured loans like a vehicle, home, or other valuables. Lenders use a credit score to approve loan applications and set terms.
A high credit score shows the lender with a strong credit history and is a low-risk borrower, leading to a better loan offer with a reduced interest rate. A low credit score suggests that the lender needs a better credit history and is a higher-risk borrower, resulting in a less attractive loan offer with a higher interest rate or the lender denying one’s loan application.
Are Unsecured Loans Easier to Get Than Secured Loans?
Yes, unsecured loans are harder to receive since a lack of collateral. Unsecured loans represent a greater risk for the lender. Thus, lenders are more selective and demand better credit ratings or financial qualifications.
Acquire an unsecured loan even with a poor credit score, but one needs to evaluate offers from various lenders. Due to the lender’s heightened risk, unsecured loans have higher interest rates.
What Is the Difference Between a Secured Loan and an Unsecured Loan?
A secured loan is a loan where the borrower pledges an asset (e.g., a vehicle, a home, or other property) as security. As such, the collateral ensures the lender gets the money back if the borrower defaults on the loan. Since the lender takes the collateral back if the borrower defaults, the interest rate and conditions of the loan are more attractive for the borrower with a secured loan.
The opposite is true for unsecured loans, which do not need any Collateral to be approved. The lender cannot confiscate any of the borrower’s assets if the borrower cannot make the necessary payments. A better credit score or other financial qualifications are needed to qualify for an unsecured loan due to the increased risk involved for the lender. Interest rates on an unsecured loan could be greater than those on a secured loan for the same reason.
Mortgages, vehicle purchases, and pawnshop loans are secured loans. Personal loans, credit card debt consolidation, and school loans fall under unsecured loans. It’s important to weigh the interest rate, payback terms, and other loan details before signing any paperwork.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is a secured loan, and how does it differ from an unsecured loan?
A secured loan requires collateral pledged against the loan, which the lender can seize if payments are not made. An unsecured loan does not require collateral, but approval is harder to obtain.
How do secured loans work, and what is the role of collateral in securing the loan?
For secured loans, the collateral like a car or property is used as assurance of repayment. If payments aren’t made, the lender takes ownership of the collateral and can sell it to cover losses. This allows more high-risk borrowers to qualify.
Why are secured loans important in the world of personal and business finance?
Secured loans allow financing for large, important purchases like homes or commercial buildings where collateral is available. This expands access to capital for individuals and businesses to grow.
What are the common types of secured loans, and how do they vary in terms of collateral and terms?
Common secured loans include mortgages (collateral is property), auto loans (collateral is the vehicle), and home equity loans (collateral is the home equity). Terms vary by loan size, collateral value, and lender.
What are the advantages and disadvantages of taking out a secured loan compared to other forms of borrowing?
Advantages include lower rates, more flexible terms, higher approval chances, and larger loan amounts. Disadvantages include risk of losing collateral if payments lapse and complicated transfer of collateral ownership.