What is a Bad Credit Score
A bad credit score is a person’s history of paying their bills on time. It shows whether they pay off their debts when they’re supposed to or if they let their debt pile up. A business’s payment practices or financial state negatively affect its creditworthiness. Payments, timely payments, and other financial mistakes lead to higher credit scores. Credit repair is crucial for borrowers to credit scores improve and maintain a good financial reputation.
Borrowing money at reasonable interest rates is challenging for individuals and businesses with bad credit. Like any high-risk borrowers, they pose a higher threat to lenders. This applies to all secured and unsecured loans, despite available options such as secured and unsecured credit cards. A secured credit card can benefit first-time users or those seeking better credit. Monitoring and maintaining a low credit utilization ratio can also aid in improving one’s credit score.
Key Takeaways
- Borrowing money becomes challenging for individuals and businesses with bad credit as they pose a higher credit risk to lenders.
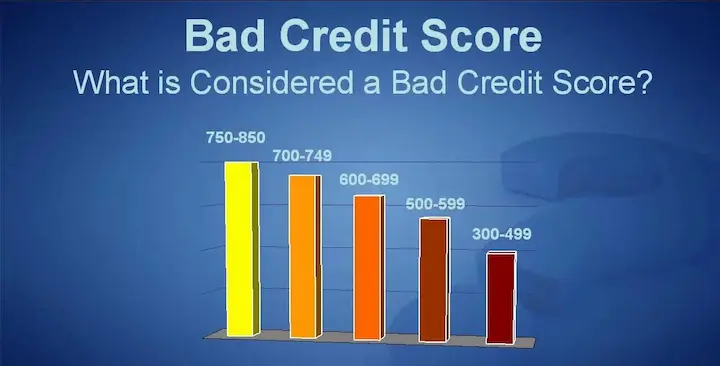
- A bad credit score reflects a person’s or a business’s payment history and financial state. The average credit score ranges from 300 to 850, with a score below 580 considered poor and 700 or higher considered good.
- Consequences of having bad credit include denial of loans, lines of credit, and higher interest rates.
- Various credit bureaus calculate the credit score based on payment records, the amount owed, length of credit history, a credit mix of credit types, and new credit.
- Improving a bad credit score involves identifying the reasons, making automatic online payments, reducing credit card debt, checking interest rate disclosures, and closing unused credit card accounts.
What is Known About Bad Credit?
A good credit risk score helps in acquiring the desired loan or employment. Average credit score ranges differ based on the model and the type of credit mix.
Potential denial of loans and lines of credit is one of the consequences. It includes mortgage, auto, private student, personal, installment, federal student loans for parents and graduate students, and credit cards. Financial institutions such as credit card issuers might only accept your applications if your credit is up to their standards.
A credit score of 700 or higher is generally regarded as good, and 800 or higher is considered an Excellent credit score, while multiple credit scoring models exist with differing score ranges.
However, the situation is improved by correcting bad credit, applying for credit-builder loans, understanding loan terms, regaining financial stability, and restoring good credit. It is worth noting that financial instability is associated with a greater likelihood of irresponsible behavior, resulting in higher insurance premiums.
Information on How a Credit Score is Computed
The credit files of most Americans who have taken loans or Types of credit are stored in one or more major credit bureaus, including Equifax, Experian, and TransUnion. These files contain information on the amount owed, payment history, and credit utilization rate, which are used to calculate their credit score. The most popular credit score in the US is the FICO score, created by the Fair Isaac Corporation.
Understanding the various types of credit available helps individuals decide which financial products best suit their needs. The FICO score serves as a measure of creditworthiness and is calculated based on the following factors. In addition to loans, credit card companies play a significant role in reporting data to these credit bureaus, making choosing reliable and reputable credit card companies essential.
- Payment record (35% weight): It shows if the person has paid their bills on time, with a higher score for better debt payment history. This includes making timely payments on any outstanding balances.
- The total amount owed (30%): It includes mortgages, credit card balances, car loans, and other debts, with a lower score for higher credit utilization rates. Applying for an Unsecured card can help with managing credit balances.
- Length of credit history (15%): The age of the oldest credit account, new credit accounts, and the average ages of all the accounts on the credit report. A well-prepared credit card application can contribute to a longer credit history.
- A mix of credit types (10%): Mortgages, car loans, and credit cards, among others. Using an Unsecured card and other types of credit can create a more diverse credit mix.
- New credit (10%): Any recent credit card application applied for or taken on.
Note: The content on payday loans, minimum payment habits, and “no credit checks” has been removed as it is irrelevant to credit scores.
What Are the Examples of Bad Credit?
There are various causes of poor credit scores, including medical bills, car accidents, job loss, etc. Some common signs of a bad credit score include the following:
- Late payment of bills
- Increased debt
- Excessive debt
- Lack of borrowing history
- Poor payment history
The FICO score ranges from 300 to 851. Borrowers with scores below 579 are considered to have poor credit, as indicated by information in their credit report.
A poor credit score results in lower credit card limits and higher interest rates and sometimes hinders job opportunities. According to Experian, 62% of borrowers with scores below 579 are at risk of becoming serious loan defaulters.
Scores between 580 and 669 are considered adequate, as these borrowers pose a lower risk of defaulting on their loans than those with poor credit scores.
What Are Some Ways to Improve a Bad Credit Score?
It is essential to identify the reasons for having a low score to improve a bad credit score. There are ways to address them, although there are various reasons. FICO provides the following recommendations:
- Consult with a personal finance expert who can help identify the factors affecting your credit score and provide tailored advice.
- Keep an eye on your credit card limits and strive to stay below them.
- Communicate with credit agencies and make sure your information is accurate and up-to-date.
- Improve your median credit score by making timely payments and keeping debt levels low.
- Consider debt consolidation options to manage your payments and reduce your interest rates.
Following these recommendations and working closely with a personal finance expert can improve your credit score and enjoy better financial opportunities.
- Automatic Online Payment: Making timely payments is crucial for improving credit scores. Missing payments can be avoided, and credit score is significantly improved by setting up automatic payments for bills and credit card payments, making credit approvals more likely.
- Credit Card Debt and Balance Transfer Credit Cards: High credit card balances negatively affect credit scores. Paying down credit card balances as much as possible and, ideally, paying them off in full each month is recommended to improve credit scores. Avoiding unnecessary purchases with credit cards is also advisable if you cannot pay off the balance each month. Using balance transfer credit cards can effectively move high-interest debt to a card with a lower interest rate, making it easier to pay off balances.
- Check Interest Rate Disclosures and Credit Card Providers: Being aware of interest rates on credit cards is important, as high-interest rates make it difficult to pay off balances. Transferring high-interest balances to a card with a lower interest rate helps reduce debt faster. Researching credit card providers and comparing their offers can help you find the lowest interest rate, ultimately saving you money.
- Unused Credit Card Accounts and Maximum Credit Limits: Closing credit card accounts negatively impact a credit score, so it is generally not recommended. However, closing them might be a good idea if there are unused credit card accounts that will not be used. The oldest accounts must be kept open to improve the average age of credit accounts and positively impact credit scores. Knowing your maximum credit limits can also help you manage your credit utilization, which is another essential factor in maintaining a healthy credit score.
Below are statistics about unused credit card accounts and maximum credit limits:
| Statistic | Value |
|---|---|
| Average number of unused credit card accounts | 2.6 |
| The average number of unused credit card accounts | $3,952 |
| Percentage of Americans with at least one unused credit card account | 70% |
| Percentage of Americans with at least two unused credit card accounts | 35% |
| Percentage of Americans with at least three unused credit card accounts | 15% |
| Percentage of Americans with at least four unused credit card accounts | 5% |
| Percentage of Americans with at least five unused credit card accounts | 2% |
| Average credit utilization ratio for Americans with unused credit card accounts | 12% |
| Average credit utilization ratio for Americans without unused credit card accounts | 20% |
Conclusion
Various methods exist to improve credit rating to enhance the chances of obtaining a loan with a low credit score. It’s crucial to understand what must be done and how.
Consistently making monthly payments on time is one of the most effective ways to enhance a borrower’s credit score. A missed payment appears late in the credit report, and maintaining timely payments on accounts positively affects the credit rating.
It is possible to negotiate with creditors and reduce the amount owed. For instance, they request to pay only half the balance when owing $1,000 but require a loan of $500. This must be accepted as creditors wish to retain customers willing to work out a repayment plan.
Another option is acquiring a personal loan or line of credit from a bank or credit union. These loans tend to have a lower interest rate than auto loans. Additionally, consider looking into online lenders as they may offer more flexible terms and rates based on an individual’s situation.
Opening Student credit cards are a good way to build credit from scratch. These products are designed for young adults with little to no credit history and can help improve your credit score with responsible usage.
Increasing your security deposit on loans or credit products can also positively affect lending decisions, as it lowers the risk taken by the lender. Furthermore, keeping your income ratio low by managing your overall debt and maintaining a stable income will make you a more attractive borrower.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is considered a bad credit score, and how does it impact my financial life?
Credit scores below 580 are generally considered bad. This can lead to higher interest rates, loan denials, lower limits, and cash security deposits. Daily finances get harder and more expensive. Bad scores take time, diligent effort and discipline to rebuild through on-time payments, lower utilization, credit mix, and avoiding new debt.
What are the common factors that can lead to a bad credit score?
Missed or late payments, high credit utilization, balances close to limits, frequent credit applications, lack of diverse credit types, foreclosures, bankruptcies, collections amounts, tax liens, judgements, and a short credit history with no positive information can all contribute to bad credit scores.
What are some effective strategies for rebuilding a bad credit score and improving my creditworthiness?
Strategies include getting current on payments, paying down balances, limiting hard inquiries, avoiding new debt, becoming an authorized user, disputing errors, and optimizing utilization by keeping it below 30%. Time and perseverance are key. Old negatives fall off reports after 7 years.
How long does it typically take to see improvements in my credit score after implementing credit-building strategies?
It depends on your starting score and factors needing repair, but most people see some improvement in 2-6 months. Significant improvement usually takes at least 12-18 months of diligent credit management. Raise your score 100 points or more within 2 years through responsible habits.
Are there any specific tools or financial products that can help me build up my credit score if it’s in poor shape?
Secured credit cards, credit builder loans, and authorized user status can help build scores from poor to fair. Balance transfer cards and credit counseling provide options. Low score mortgage programs exist. The key is maintaining responsible habits over time more than any single product.